Spring AI
官网地址:
Introduction :: Spring AI Reference
Spring AI请求流程/专有名词
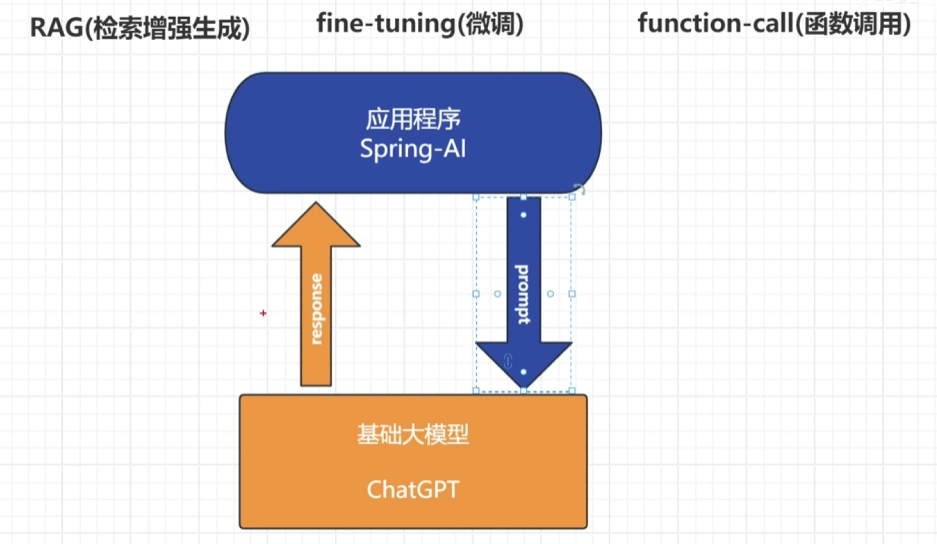
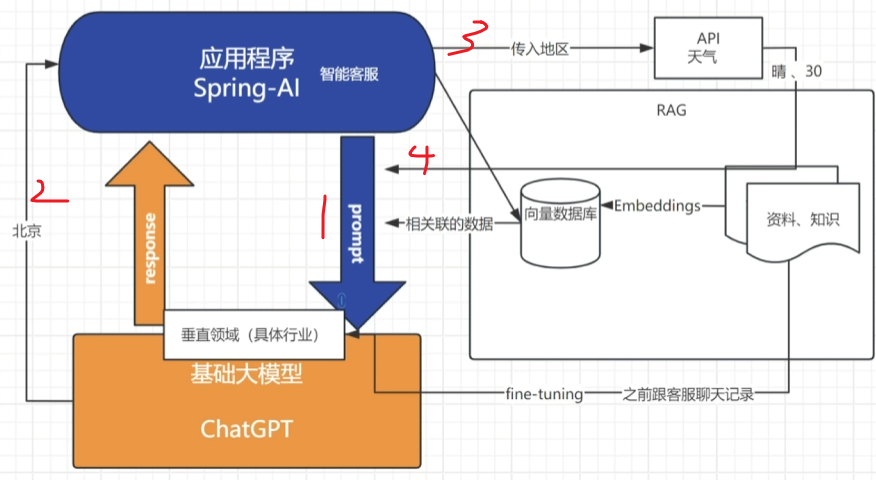
RAG:检索增强生成
大模型本身的数据可能存在一个滞后性,并且缺乏对数据的横向对比。
定义:RAG则是解决这个问题:结合信息检索技术和生成式模型的混合方法,提升自然语言处理任务(如问答、对话、内容生成等)的准确性和可靠性。
核心思想
- 检索(Retrieval): 当用户提出问题或输入指令时,系统首先从外部知识库(如文档、数据库、网页等)中检索与问题相关的上下文信息。 (例如:通过向量相似度搜索、关键词匹配等方式快速定位相关数据。)
- 生成(Generation): 将检索到的上下文与用户输入结合,输入到生成模型(如GPT、LLaMA等)中,生成最终的回答或内容。 (通过引入真实数据,减少生成模型“幻觉”问题,提升回答的准确性和可信度。)
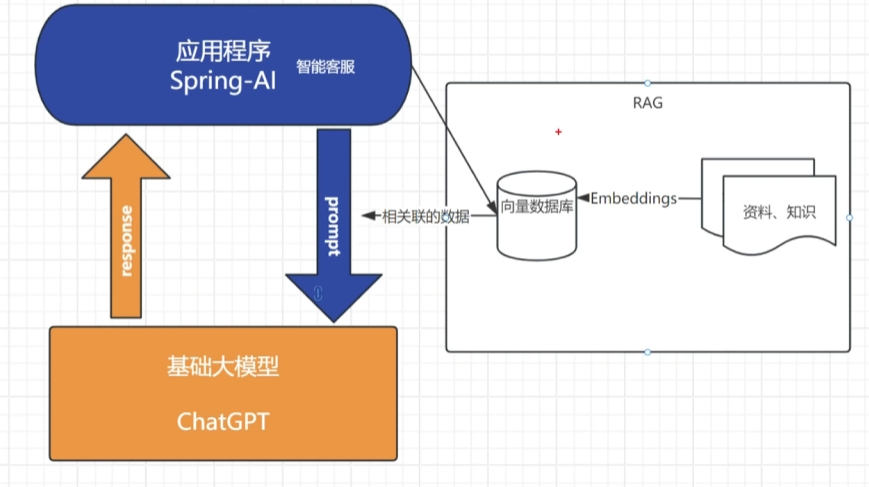
向量数据库
专门设计用于存储、管理和高效检索高维向量数据的数据库系统
主要用于处理非结构化数据(如文本、图像、音频、视频等)的向量化表示(即嵌入向量),并通过相似性搜索快速找到与查询最相关的数据。
相似性搜索的例子:
拉布拉多(特性:狗,大,叫声,性格....)我们针对每个特性进行哈希运算,就得到了拉布拉多的一串哈希值。哈希值越近的,特性越相同,越相似更容易被检索到。
fine-tuning:微调
将我们的基础大模型调教成垂直领域的模型。
将一些资料数据组成fine-tuning需要的数据格式即可进行微调
核心思想
- 预训练模型: 使用大规模通用数据(如文本、图像)训练一个基础模型,使其学习通用特征(如语言语法、图像边缘检测)。
- 任务适配: 在预训练模型的基础上,通过少量标注数据调整参数,使其专注于特定任务(如情感分析、医学图像分类)。
function-call:函数调用
一些第三方API的调用,之前spring-ai-alibaba就是这部分
ChatClient基础使用
Chat Client API :: Spring AI Reference
最基础对话
官网提供的基础示例,我们在spring-ai-alibaba也遇见过
使用默认自动化配置,创建一个ChatClient.Builder的Bean
@RestController
class MyController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public MyController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}
@GetMapping("/ai")
String generation(String userInput) {
return this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(userInput)
.call()
.content();
}
}我们也可以不使用默认的自动化配置
通过设置 spring.ai.chat.client.enabled=false 属性来禁用 ChatClient.Builder 的自动配置。 如果同时使用多个聊天模型,这会很有用。 然后,为每个需要的 ChatModel 通过编程方式创建一个 ChatClient.Builder 实例:
ChatModel myChatModel = ... // usually autowired
ChatClient.Builder builder = ChatClient.builder(this.myChatModel);
// or create a ChatClient with the default builder settings:
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.create(this.myChatModel);使用默认值(Using Defaults)
在@Configuration里创建一个带有默认文本的一个ChatClinet,能够实现将默认文本和用户输入文本结合。
例如:给他加一些前置:以老师的口吻回答(默认值)+这道题怎么解决(用户文本)
@Configuration
class Config {
@Bean
ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder.defaultSystem("You are a friendly chat bot that answers question in the voice of a Pirate")
.build();
}
}这样是一个全局的一个设置,我们也可以不使用这种方法:
通过下方的.system,单独设置系统参数,不仅仅局限于实现上面这种
@RestController
class AIController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
AIController(ChatClient chatClient) {
this.chatClient = chatClient;
}
@GetMapping("/ai")
Map<String, String> completion(@RequestParam(value = "message", defaultValue = "Tell me a joke") String message, String voice) {
return Map.of("completion",
this.chatClient.prompt()
.system(sp -> sp.param("voice", voice))//这里
.user(message)
.call()
.content());
}
}流式响应(Streaming Response)
不是直接返回结果,而是像平时问AI一样,一个字一个字吐出来。
新的数据结构:Flux<String>流式文本格式
Flux<String> output = chatClient.prompt()
.user("Tell me a joke")
.stream()
.content();但是可能会出现一个问题:就是直接返回的Flux<String>浏览器可能无法识别格式,回答出现乱码,我们可以手动给他添加: 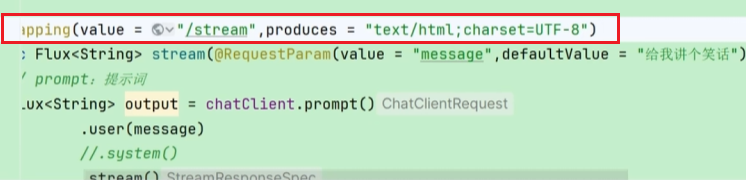
比如在@GetMapping这里添加一个响应头指明格式
ChatModel介绍
ChatClient是一个所有模型通用的一个组件。而一单想用一些独有的功能则需要我们的ChatModel
Chat Model API :: Spring AI Reference
这里面包含了几乎市面上所有的模型的一个ChatModels的使用说明。也可以直接去搜对应的文档。
使用示例:
ChatModel不需要像ChatClient一样还要我们单独配置,一般来说引入了每一家的依赖就会自动装配,所以我们直接@Autowired即可
@Autowired
private ChatModel chatModel;各家有各家的使用方法,按着文档来就行。
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"Generate the names of 5 famous pirates.",
OpenAiChatOptions.builder()
.model("deepseek-chat")
.temperature(0.4)
.build()
));PS:ChatClient底层就是封装ChatModel,并且通过一些语法糖,简化开发。
就比如最基础的ChatClient样例,直接.prompt()就行,ChatModel还得自己new Prompt()
@GetMapping("/ai")
String generation(String userInput) {
return this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(userInput)
.call()
.content();
}其他功能
Spring AI API :: Spring AI Reference
文生图,文生语音,语音翻译....这些直接看文档就行

多模态
实现当前传入的是文件,语言,或者文本。不需要我们在具体实现。
Multimodality API :: Spring AI Reference